Thumb sucking is a normal reaction in newborns and young children that gives comfort, relaxation, and security. While most children outgrow this practice by the age of four, others continue to do so into their adulthood, which may lead to oral problems. Prolonged thumb sucking may cause misalignment or damage to teeth, necessitating orthodontic intervention like braces to repair. Let’s look at how it affects teeth and how Thumb Sucking braces may help alleviate any damage that may occur.
Braces offer the smile a second chance, even for teeth once affected by thumb-sucking’s touch.
What is thumb sucking?
Thumb sucking is the practice of inserting one or both thumbs into one’s mouth and rhythmically sucking on them, as observed in infants who soothe themselves by sucking their thumbs. However, as children grow into teens, thumb sucking may persist as an unconscious behaviour during times of stress or worry, despite being frequently innocuous enough for youngsters to practice alone. At the same time, prolonged thumb sucking may have a harmful impact on tooth health.
How does thumb sucking damage your teeth?
Thumb sucking can cause misalignment of teeth and changes in jaw structure, eventually causing them to shift out of alignment, with upper front teeth protruding outward (known as open bite) or tilting inward, resulting in malocclusions that not only change appearance but also affect functionality, such as difficulty chewing and speaking. This, in turn, affects both look and function; malocclusions may impair eating and communication ability.
Thumb sucking may cause the palate to shrink and become high-arched, possibly leading to respiratory problems like snoring or sleep apnea, as well as poor tongue positioning during swallowing.
How Can Braces Help?
Braces are used to align and straighten teeth, correct malocclusions, and promote good oral health. Braces may help straighten teeth and fix bite abnormalities that have resulted from thumb sucking.
Braces may assist patients with an open bite caused by thumb sucking, progressively repositioning their teeth into suitable positions, allowing them to meet and shut properly. They may also treat additional misalignments or spacing abnormalities induced by thumb sucking, such as crowding or gaps between teeth.
Braces-based orthodontic treatment often employs brackets, wires, and, on occasion, other equipment such as rubber bands or springs to provide moderate pressure to the teeth, gradually shifting them into their intended positions. These components work together to exert a progressive force on them.
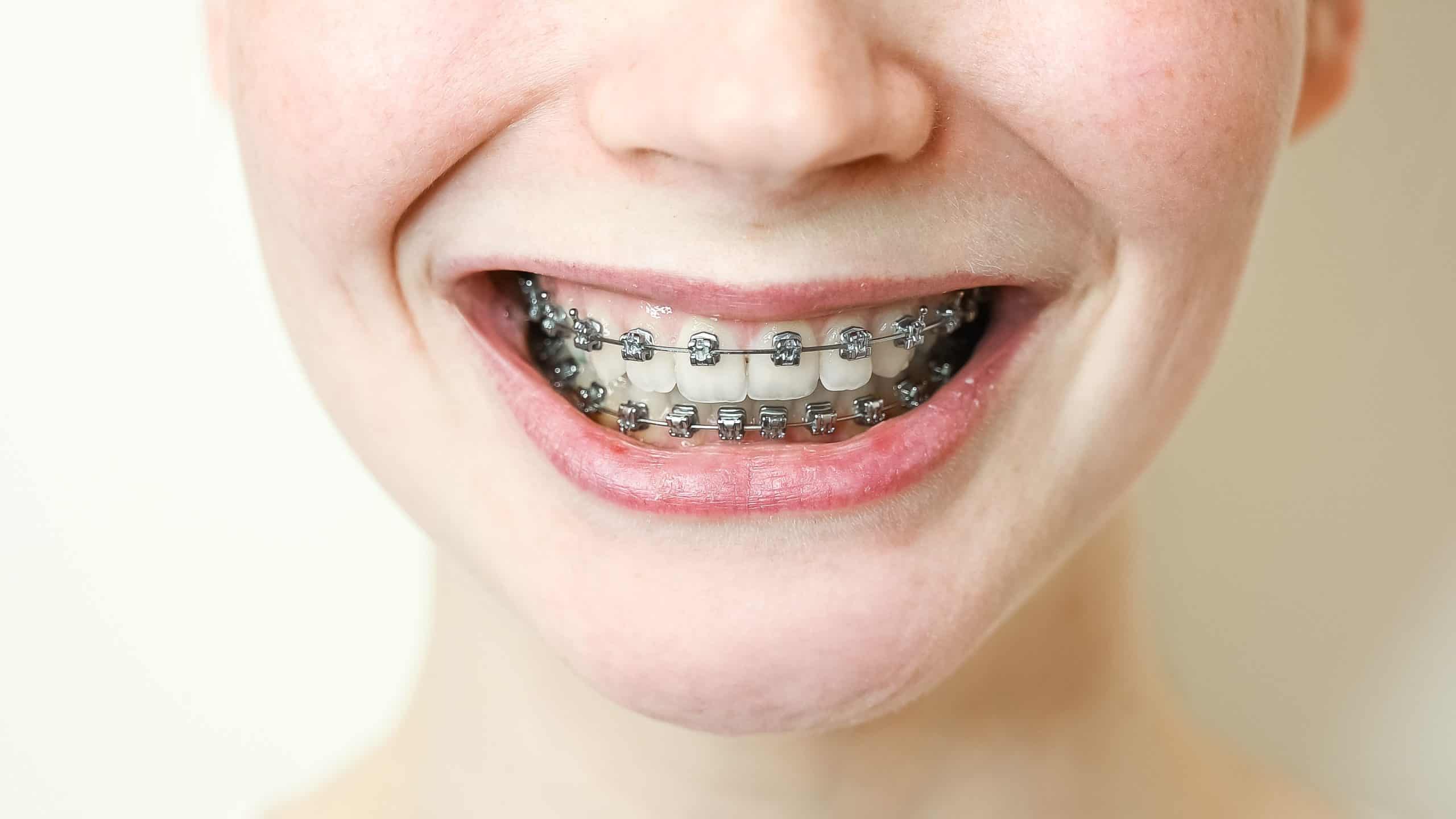
Thumb sucking consequences of 30 years old patient
Thumb sucking may seem innocent when performed by youngsters, but it may have long-term consequences if not addressed. Adult thumb suckers may have more severe dental problems because the pressure from an active jaw creates misalignment and wear and tear on their teeth.
Thumb sucking may have negative consequences, and braces may still be an effective way to address it. Although therapy may take longer than for children, braces may nonetheless help adults attain straighter, healthier smiles.
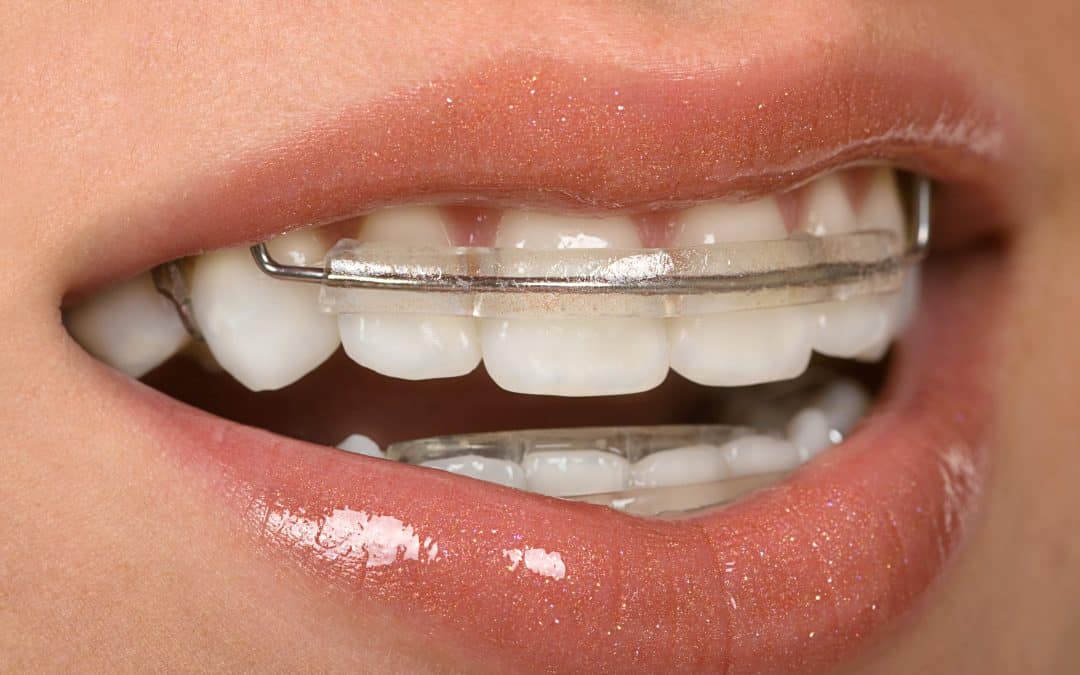
Thumb sucking consequences of 9 years old patient
Thumb sucking has a negative long-term impact on dental development. Hence, young patients need early management. Even youngsters as young as seven or eight may benefit from an orthodontic assessment if they show evidence of thumb-sucking-related tooth problems.
Orthodontists may establish suitable treatment programs for young children, including braces or other orthodontic equipment, resulting in better outcomes and less intensive orthodontic care required later.
Thumb Sucking Causes
Thumb sucking may occur for a variety of causes, such as:
Comfort and self-soothing:
Thumb sucking is a common way for infants and young children to cope with worry or stress. Its Mimicking behaviour: Children may witness others sucking their thumbs for comfort or security and then imitate this activity, sometimes unconsciously.
Boredom and inactivity:
Thumb sucking may occur during moments of boredom or inactivity for youngsters who seek stimulation via other methods. Thumb sucking may become a difficult habit to stop, even as youngsters grow into adults. Thumbsucking Treatment
Mimicking Behaviour:
Thumb sucking may often be addressed utilizing an integrated strategy that includes addressing the fundamental problems as well as changing behaviour:
Positive reinforcement:
Offering encouragement and praise to youngsters who abstain from thumb-sucking may help promote desirable habits.
Identifying triggers:
Understanding what causes thumb-sucking in youngsters, such as stress or boredom, is essential for creating alternative coping skills.
Dental Appliances:
Dentists and orthodontists may propose dental equipment, such as thumb guards or habit-breaking appliances, to reduce thumb sucking.
Counselling or Therapy:
Counseling or therapy might assist adolescents who are having difficulties stopping the habit by addressing the emotional or psychological aspects that lead to it.
Long-Term Effects and Prevention Strategies
Thumb sucking may have far-reaching consequences that go beyond dental alignment concerns, including negatively impacting speech development, facial attractiveness, and self-esteem. Long-term thumb sucking may cause speech difficulties such as lisps or trouble pronouncing specific sounds owing to changed tongue and palate posture; also, continuously pushing on the teeth and jaw may contribute to changes in facial structure, resulting in less-than-symmetrical outcomes.
Thumb sucking may have long-term ramifications; hence, early intervention or detection and correction of the behaviour is critical to limiting its detrimental effects. Parents and caregivers have an essential role in detecting and correcting this habit in newborns and young children; giving alternate comfort measures such as pacifiers or comforting items may help lessen dependency on thumb sucking as a self-soothing technique.
Conclusion
While thumb sucking for braces may cause irreversible harm to teeth and jaw development, orthodontic therapy with braces provides a remedy for these problems. Braces assist people in developing healthier, more functional smiles by addressing misalignments and biting difficulties caused by thumb sucking. Early intervention is critical for reducing the long-term impacts of thumb sucking, which emphasizes the need for appropriate orthodontic examination and treatment.